Budgeting Secrets: How to Prioritize Your Financial Goals Effectively

When it comes to personal finances, budgeting serves as the backbone for achieving financial goals. Mastering the art of budgeting can seem daunting, but it doesn’t have to be. By implementing effective strategies and prioritizing your goals methodically, you can pave the way for a more secure financial future. This article will provide you with essential insights into how to set and reach your financial objectives in a structured manner.
Firstly, it's crucial to understand the landscape of your finances. This means assessing where you're at, what your needs are, and what you aspire to achieve. Armed with this knowledge, you can make informed decisions and set clear goals subsequently.
Ultimately, the aim is to achieve a balance between your income and expenditures, leading to a more fulfilling and stress-free financial life. With that in mind, let’s dive into our key budgeting secrets that will transform your approach to managing finances.
1. Understand Your Financial Landscape

The first step in any effective budgeting process is understanding your current financial landscape. This involves analyzing your income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. Gathering this data creates a baseline from which you can build your budget and financial goals.
Notably, becoming aware of your spending habits flushes out unnecessary expenses, which may be hindering your financial progress. Once you know your current state, you can draw a clear picture of how close you are to achieving your financial aspirations.
- Create a list of all income sources.
- Document your monthly expenses including fixed and variable costs.
- Analyze your debts and their interest rates.
- Identify your assets, such as savings accounts and any investments.
By assessing where you are financially, you can establish a realistic framework that will guide your budget creation process effectively.
2. Differentiate Between Needs and Wants
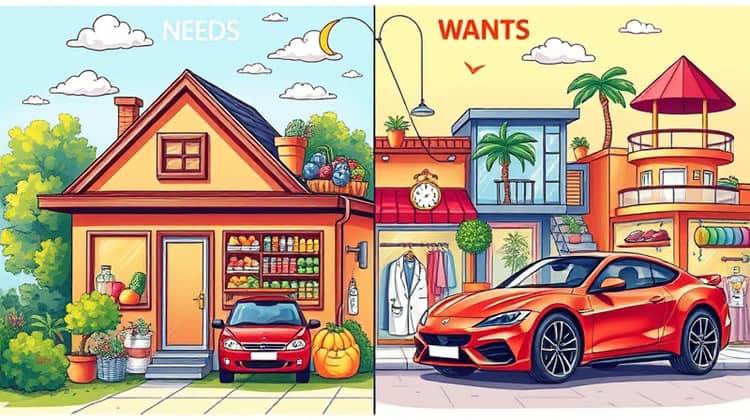

Understanding the difference between needs and wants is pivotal to creating a successful budget. Needs are essential expenses such as housing, food, transportation, and healthcare, while wants consist of the luxuries and non-essential items that can often be categorized as discretionary spending.
In budgeting, acknowledging these categories helps prioritize your spending effectively. It allows you to ensure that your needs are met before splurging on wants, ultimately saving money toward your financial goals.
- Housing costs (rent or mortgage)
- Groceries and essential household items
- Transportation costs (gas, public transport)
- Medical expenses and insurance
Once you have made this distinction, you can redirect funds typically allocated to wants to more important financial goals, enhancing your overall budget effectiveness.
3. Set SMART Financial Goals

Setting financial goals using the SMART framework ensures that your objectives are clear and attainable. SMART stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound. Each goal should be crafted with these criteria in mind to maximize your chances of success.
For instance, instead of saying, 'I want to save money,' a SMART goal would be, 'I want to save $5,000 for a vacation in 12 months by saving $417 each month.' This goal is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant to your desires, and clearly time-bound.
Formulating your goals in this structured manner prepares you for the next step in budgeting – categorizing and prioritizing your financial ambitions.
- Identify your primary financial objective: savings, debt reduction, investment, etc.
- Break down the primary goal into smaller, manageable benchmarks.
- Establish a timeline for each goal to track progress.
Through this method, you clarify your destination and create tangible steps to get there, further motivating yourself along the way.
4. Categorize Your Goals
Once you've developed SMART goals, the next strategy is to categorize them. This could include short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals, helping you visualize your financial journey.
Categorizing goals simplifies prioritization. Short-term goals might include saving for a vacation, while long-term goals could encompass saving for retirement or purchasing a home.
- Short-term goals (1 year): Emergency fund, debt repayment.
- Medium-term goals (3-5 years): Buying a vehicle, travel plans.
- Long-term goals (5 years+): Retirement savings, buying a first home.
With these categories in place, you can align your budgeting efforts with your overarching financial objectives.
5. Create an Emergency Fund

An emergency fund should be a priority in any financial plan. This fund acts as a buffer during unforeseen circumstances, such as job loss or unexpected expenses.
Setting aside a little each month ultimately protects you from derailing your financial goals.
- Aim to save at least three to six months' worth of living expenses.
- Determine a comfortable monthly contribution to reach your goal.
- Keep the funds in an easily accessible but separate account.
With a solid emergency fund, you can approach financial planning with increased confidence, knowing you’re protected in case of unexpected events.
6. Tackle High-Interest Debt First

When dealing with debt, prioritize paying off high-interest loans first, as these can grow and impact your budgeting significantly. This approach not only reduces your overall financial burden but also frees up more of your income for savings and investments.
Track and organize your debts according to interest rates, creating a focused repayment strategy that gives you clarity on how to approach your finances.
- Credit card debt
- Personal loans
- Payday loans
- Any loan with an interest rate exceeding 5%
By eliminating high-interest debt, you effectively clear a way for more efficient budgeting and financial growth in the long run.
7. Save for Retirement Early

One of the best strategies for long-term financial safety is to start saving for retirement as early as possible. The earlier you begin, the more compounding interest you’ll accumulate, which can significantly grow your savings over time.
Consider utilizing employer-sponsored retirement plans or individual retirement accounts (IRAs) to enhance your savings, while also taking advantage of any matching contributions available through your employer.
8. Break Down Your Goals

Once all your goals are categorized, the next step is to break them down into smaller actionable steps. This makes each goal feel less overwhelming and more attainable, allowing you to celebrate small successes along the way.
By breaking down goals, you can monitor progress more easily and adjust any necessary strategies.
- Set monthly targets for saving or debt repayment.
- Review progress regularly to stay motivated.
- Adjust timelines or increase contributions as circumstances change.
Being proactive in this regard propels you toward financial stability more effectively.
9. Regularly Review and Adjust

Budgeting is a dynamic process that requires regular reviews and adjustments. Financial situations change, and so should your budget. Schedule a time each month or quarter to analyze your progress toward financial goals, revisiting your categorized priorities and adjusting them as necessary.
Tracking is crucial for staying committed to your goals and maintaining clarity on your financial trajectory.
- Evaluate your income and expenditure to ensure proper tracking.
- Identify areas where you may need to cut back.
- Set new goals based on your progress and changing circumstances.
Ultimately, regular review not only fosters accountability but also ensures that your budget stays aligned with your evolving financial needs and aspirations.






